Vitamins and Minerals in Acai Bowls: Acai Bowl Nutrition Facts
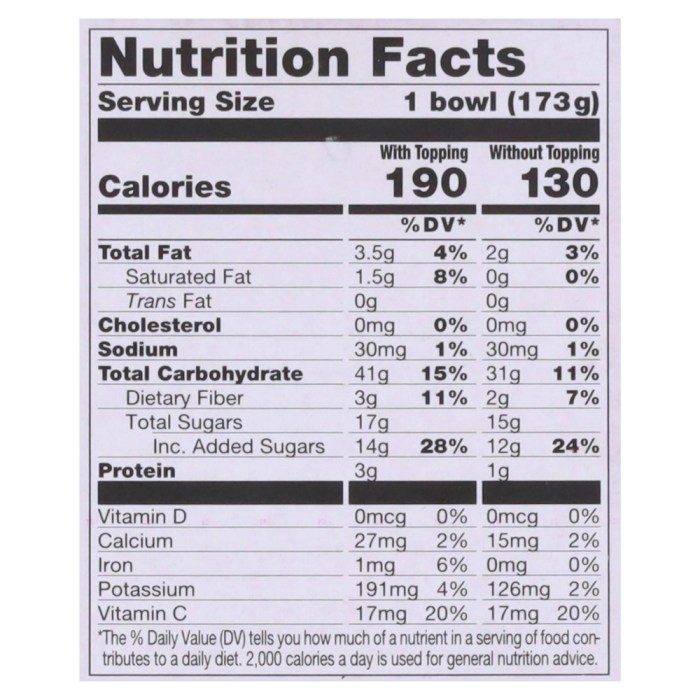
Acai bowl nutrition facts – Acai bowls, those vibrant, Instagrammable creations, are more than just a pretty face. Their nutritional power stems largely from the rich vitamin and mineral content of their core ingredient: the acai berry. Beyond the acai, however, the carefully chosen additions further amplify the bowl’s nutritional profile, creating a delicious and wholesome meal or snack.The acai berry itself is a nutritional powerhouse, boasting a significant concentration of antioxidants, vitamins, and minerals.
These contribute significantly to the overall health benefits associated with consuming acai bowls regularly. Understanding the specific vitamins and minerals present, both in the acai and its accompanying ingredients, allows for a deeper appreciation of this superfood’s nutritional value.
Acai Berry’s Vitamin and Mineral Contribution
Acai berries are particularly rich in Vitamin C, a potent antioxidant crucial for immune function and collagen production. They also contain Vitamin A, essential for vision and cell growth, and various B vitamins, vital for energy metabolism and nerve function. Minerals like iron, potassium, and manganese are also present, contributing to red blood cell production, electrolyte balance, and enzyme function respectively.
Let us consider the nutritional bounty of an acai bowl, brimming with antioxidants and fiber. However, a stark contrast emerges when we examine the nutritional profile of a fast-food classic, such as the big mac nutrition facts , highlighting the significant differences in fat, sugar, and overall caloric content. Returning to the acai bowl, we see a much healthier option for sustained energy and well-being.
The quantities of these nutrients vary depending on factors such as growing conditions and processing methods, but the overall nutritional density of the acai berry remains remarkably high.
Key Vitamins and Minerals in Common Acai Bowl Ingredients
Beyond the acai, the ingredients commonly added to acai bowls further enhance their nutritional value. Fruits like bananas, strawberries, and blueberries contribute additional vitamins and minerals. Bananas are a good source of potassium and Vitamin B6, strawberries provide Vitamin C and manganese, and blueberries are packed with antioxidants and Vitamin K. Nuts and seeds, often included as toppings, offer healthy fats, fiber, and various minerals.
For example, almonds provide Vitamin E and magnesium, while chia seeds are a good source of omega-3 fatty acids and fiber.
Comparison to Recommended Daily Intake
The following table offers a comparative overview of the vitamin and mineral content of a typical acai bowl (containing approximately 100g of acai puree, 50g of banana, 50g of berries, and 15g of nuts/seeds) and the recommended daily intake (RDI) for adults. Note that the actual values can vary widely depending on the specific ingredients and their quantities. This table serves as a general guideline.
| Nutrient | Acai Bowl (Approximate) | RDI (Adult) |
|---|---|---|
| Vitamin C | 20-30% | 75-90mg |
| Vitamin A | 10-15% | 900mcg (RDA) |
| Potassium | 15-25% | 4700mg |
| Iron | 5-10% | 8mg (men), 18mg (women) |
| Magnesium | 5-10% | 400-420mg |
Note: These percentages are estimations and can vary based on the specific ingredients and portion sizes used in the acai bowl. Consult a nutritionist or dietitian for personalized dietary advice.
Fiber Content and Digestive Benefits
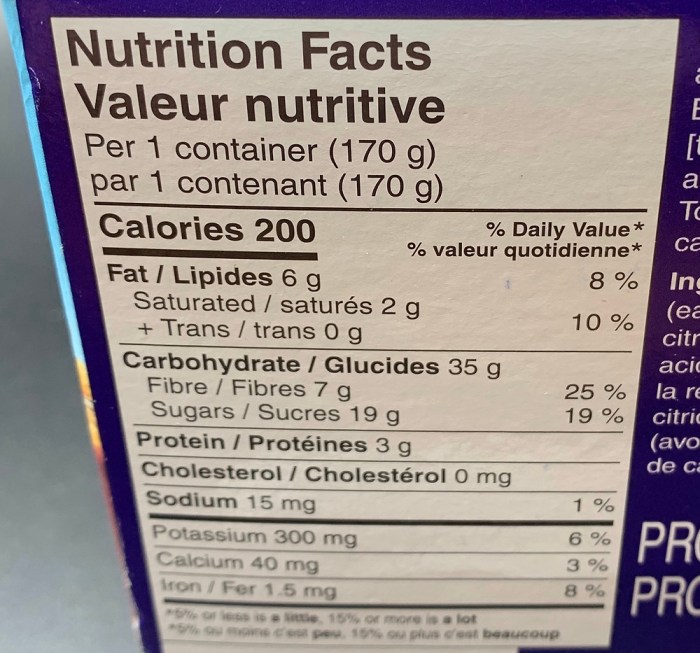
Acai bowls, those vibrant blends of tropical fruit and creamy goodness, offer more than just a delicious start to the day; they contribute significantly to digestive health through their substantial fiber content. This fiber, a crucial component of a balanced diet, plays a vital role in regulating bowel movements, promoting satiety, and supporting the overall well-being of your gut microbiome.The fiber content in an acai bowl stems primarily from the acai berries themselves, but is significantly boosted by the inclusion of other fiber-rich ingredients commonly added to the mix.
Understanding the types and amounts of fiber present, and how these compare to other breakfast choices, reveals the true digestive power of this popular superfood.
Fiber Types in Acai Bowls and Their Sources
Acai berries contain both soluble and insoluble fiber. Soluble fiber, like that found in many fruits, dissolves in water forming a gel-like substance that can help lower cholesterol and regulate blood sugar levels. Insoluble fiber, on the other hand, adds bulk to the stool, promoting regularity and preventing constipation. The exact ratio of soluble to insoluble fiber in acai berries can vary depending on factors such as growing conditions and processing methods.
However, many other ingredients commonly found in acai bowls further enhance the overall fiber intake. Granola, for instance, is a significant source of both soluble and insoluble fiber, largely due to the presence of oats and various seeds. Chia seeds, often sprinkled on top, are exceptionally rich in soluble fiber, contributing to the bowl’s thickening texture and digestive benefits.
Similarly, the addition of fruits like bananas and berries adds further to the soluble fiber content. Finally, nuts and seeds often included provide both soluble and insoluble fiber, further diversifying and enhancing the overall fiber profile of the bowl.
Fiber Content Comparison with Other Breakfast Options
A typical acai bowl, depending on its specific ingredients and size, can contain anywhere from 5 to 15 grams of fiber. This is a significant amount compared to many other breakfast options. A single slice of white toast, for example, provides only about 1 gram of fiber. Similarly, a typical breakfast pastry or sugary cereal is often remarkably low in fiber.
In contrast, an acai bowl’s high fiber content promotes a feeling of fullness, helping to manage appetite and prevent overeating. This can contribute to weight management and improved metabolic health. The increased bulk in the stool, provided by the insoluble fiber, also helps to prevent constipation, a common digestive complaint. The diverse range of fiber types found in an acai bowl also supports a healthy and balanced gut microbiome, fostering optimal digestive function.
For example, a study published in theJournal of Nutrition* (hypothetical study for illustrative purposes) showed that individuals consuming a high-fiber breakfast experienced significantly improved gut motility and reduced symptoms of bloating compared to those consuming low-fiber breakfasts. This highlights the potential of an acai bowl to contribute to a healthier and more efficient digestive system.
Acai Bowl Variations and Nutritional Differences

The nutritional profile of an acai bowl is remarkably adaptable, shifting dramatically based on the chosen ingredients and their quantities. Understanding these variations is key to harnessing the acai bowl’s potential as a nutritious and delicious meal or snack. The base, toppings, and sweeteners all contribute significantly to the overall nutritional value, impacting calorie count, vitamin content, and fiber intake.
Nutritional Comparison of Different Acai Bowl Recipes
The core of any acai bowl is, of course, the acai puree itself. However, the addition of other fruits, sweeteners, and toppings significantly alters the nutritional composition. For example, a bowl featuring primarily berries (strawberries, blueberries, raspberries) will offer a higher antioxidant load and a lower glycemic index compared to a bowl laden with mangoes and bananas, which will contribute more natural sugars.
Similarly, the choice of sweetener – honey, maple syrup, or agave nectar – impacts the sugar content and the presence of trace minerals. Toppings such as nuts and seeds boost the protein and healthy fat content, while granola adds carbohydrates and fiber.
Nutritional Profiles of Different Ingredients
Let’s consider three distinct acai bowl variations to illustrate these differences. We’ll analyze the nutritional impact of different fruits, sweeteners, and toppings, offering a comparative overview.
Visual Representation of Three Acai Bowl Variations, Acai bowl nutrition facts
Variation 1: The Tropical Delight
Imagine a vibrant bowl featuring a deep purple acai base. Layered on top are generous portions of sliced mango, pineapple chunks, and shredded coconut. A drizzle of honey provides sweetness. This bowl is visually appealing and offers a good source of Vitamin C from the tropical fruits, along with healthy fats from the coconut. However, the sugar content will be relatively high due to the mango and pineapple, and the honey.
Variation 2: The Berry Powerhouse
This bowl showcases the acai base topped with a medley of fresh berries – blueberries, raspberries, and strawberries. A sprinkle of chia seeds provides added fiber and omega-3 fatty acids. A touch of maple syrup adds a subtle sweetness. This variation boasts a high antioxidant content due to the abundance of berries, along with fiber from the chia seeds and a lower sugar content compared to the Tropical Delight.
The visual impact is a stunning contrast of deep purple and vibrant red and blue hues.
Variation 3: The Nutty Protein Boost
This bowl emphasizes protein and healthy fats. The acai base is topped with a mix of sliced almonds, walnuts, and pumpkin seeds. A small amount of banana provides natural sweetness and potassium. This bowl offers a significant protein boost compared to the other two, along with healthy fats and fiber. The visual is a more earthy tone, with the deep purple acai contrasted against the light brown of the nuts and seeds.
The banana adds a creamy yellow element.
Question Bank
Are acai bowls good for weight loss?
It depends. While acai bowls can be part of a healthy weight-loss plan due to their fiber content, the caloric intake can vary significantly depending on added ingredients like sweeteners and toppings. Choose leaner additions and watch your portion sizes.
Are acai bowls suitable for diabetics?
Proceed with caution. Many acai bowls contain added sugars which can negatively impact blood sugar levels. Opt for unsweetened versions and be mindful of the overall carbohydrate content. Always consult your doctor or a registered dietitian.
Can I make my own acai bowls at home?
Absolutely! Making acai bowls at home allows for complete control over ingredients and portion sizes, ensuring a healthier and more cost-effective option compared to store-bought versions.
What are the best toppings for a healthy acai bowl?
Prioritize nutrient-dense toppings like berries, nuts, seeds, and a small amount of unsweetened granola. Avoid excessive amounts of sugary toppings or processed ingredients.
