Nutritional Composition of Orange Juice

Orange juice nutrition facts – Orange juice, a vibrant and refreshing beverage, offers a surprising array of nutritional benefits beyond its delightful taste. A closer examination reveals a complex profile of vitamins, minerals, and other beneficial compounds that contribute to its overall health-promoting properties. This exploration delves into the detailed nutritional composition of orange juice, providing a clearer understanding of its impact on well-being.
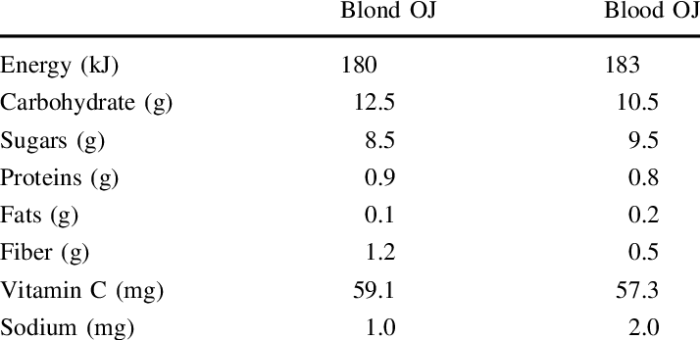
Macronutrient Content of Orange Juice
A typical 8-ounce (240ml) serving of orange juice provides a moderate source of carbohydrates, primarily in the form of natural sugars. These sugars contribute to the juice’s sweetness and provide readily available energy. While containing some protein, orange juice is not a significant source of this macronutrient. Fat content is negligible. The exact values can vary slightly depending on the type of orange and processing methods.
However, a reasonable approximation for a standard serving includes approximately 20-25 grams of carbohydrates, including 18-22 grams of sugar, less than 1 gram of protein, and less than 0.5 grams of fat.
Vitamin and Mineral Profile of Orange Juice
Orange juice is particularly rich in several essential vitamins and minerals, playing a vital role in maintaining overall health. The following table summarizes the key nutrients found in a typical 8-ounce serving, alongside their approximate daily value percentages and associated health benefits. Note that the percentages are based on a 2,000-calorie diet and may vary depending on individual needs.
Orange juice, a popular breakfast beverage, offers a good source of Vitamin C and potassium. However, its sugar content can be a concern for some. For a healthier alternative with sustained energy, consider exploring the nutritional profile of almond butter nutrition facts , which provides healthy fats and protein. Ultimately, balancing orange juice with other nutritious foods like almonds creates a more well-rounded diet.
| Name | Amount per serving | % Daily Value | Health Benefit |
|---|---|---|---|
| Vitamin C | 90-100mg | 100-110% | Supports immune function, acts as an antioxidant. |
| Potassium | 200-250mg | 5-7% | Maintains healthy blood pressure, supports muscle function. |
| Folate | 20-30mcg | 5-8% | Essential for cell growth and development, crucial during pregnancy. |
| Thiamin | 0.1-0.2mg | 7-14% | Supports energy metabolism and nerve function. |
| Magnesium | 10-15mg | 2-4% | Contributes to bone health and muscle function. |
Phytochemicals and Antioxidants in Orange Juice
Beyond vitamins and minerals, orange juice contains a variety of phytochemicals and antioxidants, which contribute to its potential health benefits. These compounds, naturally occurring in plants, possess potent antioxidant properties that combat free radicals, protecting cells from damage and reducing the risk of chronic diseases. For instance, flavonoids like hesperidin and naringenin are abundant in oranges and their juice, exhibiting anti-inflammatory and cardiovascular protective effects.
These antioxidants help reduce the risk of heart disease and certain cancers by neutralizing harmful free radicals. The synergistic effect of these various compounds contributes significantly to the overall nutritional value of orange juice.
Orange Juice and Health Benefits: Orange Juice Nutrition Facts

The vibrant, tangy elixir we know as orange juice offers more than just a refreshing taste; it’s a nutritional powerhouse brimming with potential health benefits. A daily glass might seem like a simple pleasure, but the impact on our well-being could be surprisingly significant, a secret whispered by the citrus groves themselves. Let’s delve into the intriguing mysteries surrounding this seemingly ordinary juice.Orange juice’s contribution to health extends far beyond simple hydration.
Its rich profile of vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants plays a multifaceted role in supporting various bodily functions, influencing everything from our immune response to our cardiovascular system. The enigmatic nature of these benefits lies in the synergistic action of these components, a carefully orchestrated symphony within each glass.
Immune System Support
Vitamin C, a prominent star in the orange juice ensemble, is a potent antioxidant known for its role in bolstering the immune system. Studies have shown that adequate Vitamin C intake can help reduce the duration and severity of common colds. For example, a meta-analysis published in theJournal of the American College of Nutrition* reviewed numerous studies and concluded that supplemental Vitamin C may reduce the risk of respiratory infections.
This is particularly relevant during cold and flu season, when the body’s defenses are challenged. Further research continues to unravel the intricate ways in which Vitamin C and other antioxidants in orange juice interact with the immune system, promising even deeper understanding of its protective effects.
Cardiovascular Health
The relationship between orange juice consumption and cardiovascular health is a complex, yet intriguing tale. While some concerns exist regarding added sugars in commercially produced juices, the inherent nutrients within the juice itself often contribute positively. Studies suggest that the potassium content in orange juice can help regulate blood pressure. Furthermore, certain compounds in citrus fruits, including those found in oranges, have demonstrated potential in improving cholesterol profiles.
However, it’s crucial to remember that orange juice should be consumed as part of a balanced diet and lifestyle. Relying solely on orange juice for cardiovascular benefits would be an oversimplification of a complex interplay of factors. Moderation, as with all things, is key to unlocking its potential benefits.
Overall Well-being
Beyond specific systems, the nutrients in orange juice contribute to a general sense of well-being. The natural sugars provide a quick energy boost, beneficial for those needing a midday pick-me-up. The fiber content, although relatively low compared to whole fruits, can still aid in digestive health by promoting regularity. Moreover, the presence of various phytochemicals adds another layer of complexity to its beneficial properties, contributing to the overall antioxidant capacity and potentially offering protection against chronic diseases.
It’s the subtle interplay of these various elements, a secret recipe known only to nature, that truly contributes to overall health and vitality.
Potential Drawbacks of Orange Juice Consumption
While orange juice offers numerous health benefits, excessive consumption can lead to several drawbacks. The seemingly innocuous glass of sunshine can harbor hidden pitfalls for those unaware of its potential downsides. Let’s delve into the less-than-sunny aspects of this popular beverage.The primary concern revolves around its high sugar content. A single glass can contain a significant amount of natural sugars, contributing to overall daily sugar intake and potentially leading to various health issues.
This is particularly relevant in the context of weight management and metabolic health.
High Sugar Intake and Dental Issues
The naturally occurring sugars in orange juice, while different from refined sugars, still contribute to the risk of dental problems. The sugars feed bacteria in the mouth, producing acids that erode tooth enamel, increasing the likelihood of cavities and gum disease. The acidity of the juice itself can also contribute to enamel erosion. Regular consumption of orange juice, especially without proper oral hygiene, can significantly increase these risks.
Consider the example of a child consuming multiple glasses daily; the cumulative effect over time could be substantial.
Impact on Blood Sugar Levels, Orange juice nutrition facts
Orange juice’s high sugar content directly impacts blood glucose levels. The rapid absorption of fructose and glucose can cause a sudden spike in blood sugar, followed by a subsequent crash. This is particularly problematic for individuals with diabetes or those at risk of developing the condition. For instance, a person with type 2 diabetes might experience uncontrolled blood sugar levels after consuming a large glass of orange juice, potentially leading to complications.
Careful monitoring and moderation are crucial.
Allergic Reactions and Sensitivities
Although relatively rare, allergic reactions to orange juice are possible. These reactions can range from mild symptoms like skin rashes and itching to more severe reactions, including anaphylaxis. Sensitivity to citric acid, a component of orange juice, is also relatively common, causing digestive discomfort such as heartburn or stomach upset in susceptible individuals. These reactions can vary widely in severity and individual responses.
A person with a known citrus allergy should obviously avoid orange juice entirely.
FAQ
Is orange juice good for weight loss?
Orange juice can be part of a weight-loss diet, but its sugar content should be considered. Opt for smaller servings and be mindful of overall calorie intake.
Can I drink orange juice if I have acid reflux?
Citrus fruits like oranges can exacerbate acid reflux in some individuals. Consume in moderation and monitor your symptoms.
Does orange juice interact with any medications?
Some medications may interact with the components in orange juice. Consult your doctor or pharmacist if you have concerns.
Is it better to drink freshly squeezed or from concentrate orange juice?
Freshly squeezed typically retains more nutrients, but from-concentrate options are often more affordable and readily available. Read labels carefully to compare nutritional profiles.
