Gatorade G2 vs. Other Sports Drinks
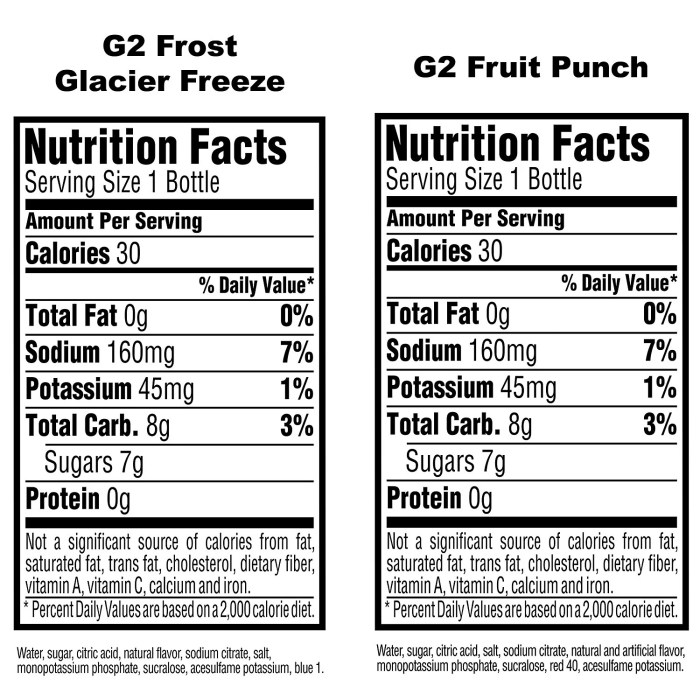
Gatorade g2 nutrition facts – Gatorade G2, marketed as a lower-sugar alternative to its original formula, occupies a specific niche within the sports drink market. Comparing it to competitors requires a detailed examination of its sugar content, electrolyte profile, and overall nutritional composition. This analysis will highlight key distinctions and aid in informed consumer choices.
Sugar Content Comparison
Gatorade G2 boasts a significantly reduced sugar content compared to many traditional sports drinks. While the exact amount varies depending on flavor and serving size, it generally contains considerably less sugar than its competitors such as Gatorade (original), Powerade, and even some “enhanced water” brands. This lower sugar content is a major selling point for consumers seeking to reduce their overall sugar intake.
The lower sugar content may also be beneficial for individuals concerned about the potential negative effects of high sugar consumption on athletic performance and overall health.
Electrolyte Balance Differences, Gatorade g2 nutrition facts
While G2 has less sugar, the balance of electrolytes—sodium, potassium, chloride—remains a crucial factor in replenishing fluids and minerals lost during physical activity. While the precise electrolyte ratios differ between brands and flavors, a comparison would show that G2 generally maintains a sufficient electrolyte profile to support hydration and electrolyte replenishment, though possibly at a slightly lower concentration than some higher-sugar competitors.
The reduced sugar content in G2 does not necessarily compromise its effectiveness in electrolyte replenishment for moderate exercise.
Key Nutritional Differences
Beyond sugar and electrolytes, other nutritional differences exist. G2 typically contains fewer calories than many of its competitors due to its lower sugar content. It also often features artificial sweeteners and colors, a distinction that some consumers may consider when comparing products. Some competitors may offer additional vitamins or minerals, but G2 focuses on a simpler electrolyte and carbohydrate profile.
This simplicity is part of its marketing appeal.
Calorie Count Comparison
The following bullet points compare the calorie count of a typical serving size (approximately 20 ounces) of Gatorade G2 to three competitor products. Note that precise values can vary based on flavor and serving size. These values are estimates based on readily available product information and may differ slightly depending on the specific product and packaging.
- Gatorade G2: Approximately 30-40 calories
- Gatorade (Original): Approximately 80-100 calories
- Powerade: Approximately 80-100 calories
- Propel (Enhanced Water): Approximately 10-20 calories
Gatorade G2 and Hydration
Gatorade G2, a low-calorie sports drink, offers a blend of electrolytes and carbohydrates designed to support hydration and energy replenishment during physical activity. Understanding its composition and how it interacts with the body is crucial to determining its suitability for various hydration needs.
Electrolyte Contribution to Hydration
Electrolytes, including sodium, potassium, and chloride, are essential minerals that play a vital role in fluid balance within the body. When we sweat during exercise, we lose these electrolytes along with water. Gatorade G2’s electrolyte content helps to replace these lost minerals, facilitating better fluid absorption and retention compared to plain water alone. This is because the presence of electrolytes enhances the movement of water across cell membranes, promoting rehydration and preventing dehydration-related symptoms such as muscle cramps and fatigue.
The specific concentrations of electrolytes in G2 are designed to support this process without causing excessive sodium intake.
Carbohydrate Role in Energy Replenishment
Gatorade G2 contains carbohydrates, primarily in the form of sugars like glucose and fructose. During prolonged or intense physical activity, the body’s glycogen stores (stored carbohydrates) become depleted. The carbohydrates in G2 provide a readily available source of energy to replenish these stores and help maintain blood glucose levels, delaying fatigue and improving endurance. The combination of carbohydrates and electrolytes helps the body efficiently utilize the available glucose for energy production.
This is particularly important during activities lasting longer than 60 minutes.
Situations Favoring Gatorade G2 over Plain Water
While plain water is sufficient for hydration during short, low-intensity activities, Gatorade G2 offers advantages in specific scenarios. Prolonged exercise (lasting longer than 60 minutes), high-intensity workouts, and activities in hot and humid conditions lead to significant fluid and electrolyte loss. In these situations, plain water may not be sufficient to replace both the water and electrolyte losses, making G2 a more appropriate choice.
Gatorade G2 is a lower-calorie sports drink, but it’s important to check the nutrition facts before you guzzle it down. If you’re looking for something completely different, you might want to compare it to something like a hearty breakfast, and check out the nutrition facts for biscuits and gravy for a contrast. Then you can make an informed choice about what fits your nutritional goals, whether it’s the electrolyte boost of G2 or the caloric richness of biscuits and gravy.
Similarly, individuals who experience significant sweating during exercise may benefit from the electrolyte replenishment provided by G2 to prevent dehydration-related symptoms.
Gatorade G2 for Hydration During Exercise: Pros and Cons
| Type of Exercise | Pros of Using Gatorade G2 | Cons of Using Gatorade G2 |
|---|---|---|
| Short, Low-Intensity (e.g., 30-minute walk) | Minimal benefit; plain water is sufficient. | Unnecessary sugar and calorie intake. |
| Moderate-Intensity (e.g., 1-hour jog) | Replenishes some fluid and electrolyte loss; provides a small energy boost. | May contribute to excess sugar intake for some individuals. |
| High-Intensity, Prolonged (e.g., marathon) | Significant fluid and electrolyte replenishment; sustained energy supply. | High sugar content may cause gastrointestinal distress in some individuals. |
| Exercise in Hot/Humid Conditions | Improved hydration due to electrolyte content; helps prevent heat exhaustion. | Potential for excessive sugar intake; consider individual tolerance. |
Gatorade G2 and Health Considerations
Gatorade G2, while marketed as a lower-sugar sports drink, still contains added sugars and sodium, raising potential health concerns with regular consumption. Understanding the potential implications for various individuals and exploring healthier alternatives is crucial for informed choices.Regular consumption of Gatorade G2, even in moderation, can contribute to excessive sugar intake. High sugar intake is linked to weight gain, increased risk of type 2 diabetes, and other metabolic disorders.
The sodium content, while lower than in original Gatorade, can also be a concern for individuals with hypertension or other sodium-sensitive conditions. Furthermore, the reliance on artificial sweeteners in some G2 varieties warrants further investigation into their long-term health effects.
Added Sugars and Sodium’s Impact on Health
Excessive sugar consumption is associated with a multitude of health problems. Added sugars contribute to weight gain and obesity, increasing the risk of developing chronic diseases such as type 2 diabetes, cardiovascular disease, and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. The American Heart Association recommends limiting added sugar intake to no more than 25 grams per day for women and 36 grams per day for men.
Similarly, excessive sodium intake is a major risk factor for high blood pressure (hypertension), a leading cause of heart disease and stroke. The Dietary Guidelines for Americans recommend limiting sodium intake to less than 2,300 milligrams per day. Gatorade G2, while lower in sugar and sodium than its original counterpart, still contains both, necessitating mindful consumption.
Gatorade G2 and Specific Dietary Restrictions or Health Conditions
Individuals with diabetes should exercise extreme caution when consuming Gatorade G2. The added sugars, even in reduced amounts, can significantly impact blood glucose levels. Careful monitoring of blood sugar is essential, and consultation with a healthcare professional or registered dietitian is recommended before incorporating G2 into a diabetic diet. Similarly, those with kidney disease should be mindful of both the sugar and sodium content, as these can exacerbate existing kidney problems.
The high phosphorus content in some sports drinks, including some varieties of Gatorade G2, might also be problematic for individuals with kidney issues. It is crucial for these individuals to consult with their nephrologist or dietitian before consumption.
Alternative Hydration Strategies
Plain water remains the most effective and healthiest hydration strategy for most individuals. Unsweetened tea, infused water with fruits and vegetables, and diluted fruit juices are healthier alternatives to sports drinks. These options provide hydration without the added sugars and sodium found in Gatorade G2. For individuals engaged in intense physical activity, coconut water can be a suitable option due to its electrolyte content.
However, it’s important to note that even coconut water contains natural sugars. The choice of hydration strategy should be tailored to individual needs and activity levels.
Recommendations for Responsible Gatorade G2 Consumption
To minimize potential health risks associated with Gatorade G2 consumption, the following recommendations are suggested:
- Consume Gatorade G2 sparingly and only when needed, such as during or after prolonged or intense physical activity.
- Choose lower-sugar options whenever possible, paying close attention to the nutrition label.
- Monitor your blood glucose levels regularly if you have diabetes.
- Consult with a healthcare professional or registered dietitian before incorporating Gatorade G2 into your diet, especially if you have any underlying health conditions.
- Prioritize hydration primarily through plain water and other healthier alternatives.
- Be aware of the sodium content and consider its impact on your blood pressure.
FAQ Overview: Gatorade G2 Nutrition Facts
Is Gatorade G2 suitable for diabetics?
Due to its sugar content, diabetics should exercise caution and consult their doctor before regular consumption. Look for sugar-free alternatives or opt for smaller servings.
Can I use Gatorade G2 for everyday hydration?
Not recommended. Plain water is generally the best choice for everyday hydration. Gatorade G2 is best suited for intense physical activity where electrolyte replenishment is crucial.
Does Gatorade G2 contain artificial sweeteners?
Check the specific label, as formulations can vary. Some versions may contain artificial sweeteners.
How does Gatorade G2 compare to coconut water?
Coconut water is naturally lower in sugar and sodium than Gatorade G2, but may not contain the same levels of other electrolytes.
