Health Benefits Associated with Seaweed Salad Consumption

Seaweed salad nutrition facts – Seaweed salad, a culinary delight enjoyed across various cultures, offers a surprising array of health benefits beyond its palatable taste. Its nutritional profile, rich in vitamins, minerals, and bioactive compounds, contributes significantly to overall well-being. This section will delve into the specific health advantages associated with regular seaweed salad consumption, focusing on its impact on cardiovascular health, immune function, and inflammatory processes.
Cardiovascular Health Benefits of Seaweed Salad
Seaweed salad’s contribution to cardiovascular health stems primarily from its ability to influence blood pressure and cholesterol levels. Many seaweed varieties are rich in potassium, a mineral that helps counter the effects of sodium, thereby promoting healthy blood pressure. Furthermore, certain types of seaweed contain compounds that can help lower LDL (“bad”) cholesterol levels, reducing the risk of atherosclerosis and related cardiovascular diseases.
The soluble fiber present in seaweed also contributes to lowering cholesterol by binding to it in the digestive tract, preventing its absorption into the bloodstream. Studies have shown correlations between regular seaweed consumption and improved cardiovascular markers in some populations, although further research is needed to establish definitive causal links.
Seaweed Salad’s Role in Supporting Immune Function, Seaweed salad nutrition facts
Seaweed salad is a valuable source of various vitamins and minerals crucial for a robust immune system. Vitamin C, a potent antioxidant, is abundant in some seaweed varieties and plays a vital role in immune cell function. Similarly, seaweed is a good source of iodine, an essential mineral for thyroid hormone production, which is crucial for immune regulation.
Furthermore, seaweed contains various other vitamins and minerals, such as vitamin A, vitamin K, and zinc, all contributing to the body’s overall defense mechanisms. The presence of antioxidants in seaweed also helps combat oxidative stress, a factor that can compromise immune function.
Anti-inflammatory Properties of Seaweed Salad and its Impact on Chronic Diseases
Seaweed contains various bioactive compounds, including polysaccharides and polyphenols, that exhibit anti-inflammatory properties. Chronic inflammation is implicated in the development of many chronic diseases, such as heart disease, arthritis, and certain types of cancer. By reducing inflammation, seaweed consumption may play a role in mitigating the risk or progression of these conditions. While research in this area is ongoing, preliminary studies suggest a potential link between seaweed consumption and reduced inflammatory markers in the body.
Seaweed salad offers a unique nutritional profile, rich in vitamins and minerals. For a different perspective on nutrient-dense foods, consider exploring the comprehensive details on egg yolk nutrition facts , which highlight a contrasting source of vital nutrients. Returning to seaweed salad, its low-calorie nature and abundance of iodine make it a valuable addition to a balanced diet.
Further research is needed to solidify these findings and elucidate the mechanisms involved.
Comparative Nutritional Value and Health Benefits of Different Seaweed Types
Several types of seaweed are commonly used in seaweed salad, each possessing a unique nutritional profile and associated health benefits. A comparison is crucial for understanding the variations in their contribution to overall health.
- Wakame: Rich in fiber, vitamins (A, C, K), and minerals (calcium, iron, iodine). Known for its potential to lower cholesterol and improve gut health.
- Nori: Excellent source of protein, fiber, and various vitamins and minerals, including vitamin B12 (relatively rare in plant-based foods). Often consumed as sheets, but also found in salads.
- Arame: High in minerals, particularly calcium and iron. Contains alginate, a type of fiber with potential cholesterol-lowering properties. Possesses a milder flavor compared to wakame or nori.
While all three offer significant health benefits, the specific nutritional composition varies, allowing individuals to choose based on their dietary preferences and health goals. For example, individuals needing a vitamin B12 boost might favor nori, while those focusing on calcium intake may choose arame.
Seaweed Salad and Weight Management
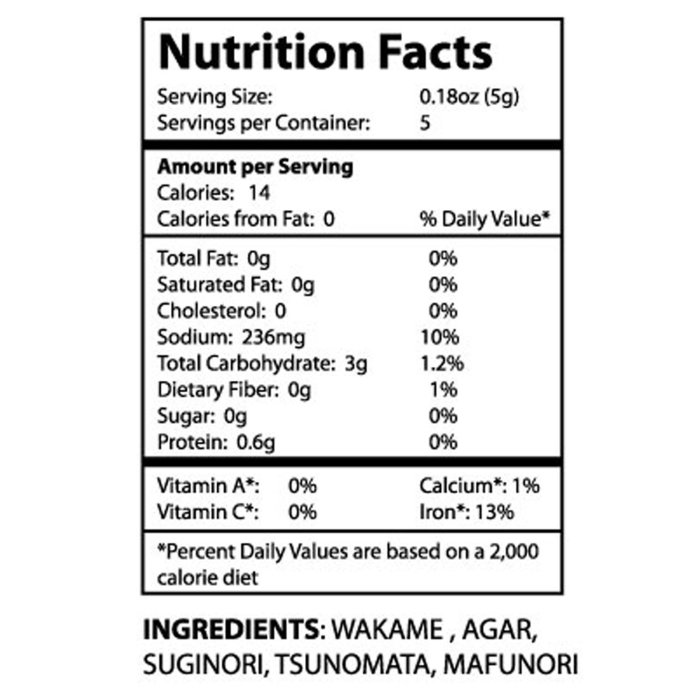
Seaweed salad can be a valuable component of a balanced diet designed for weight management. Its low calorie density, coupled with its high fiber and water content, contributes to satiety, helping individuals feel fuller for longer and potentially reducing overall calorie intake. This, in turn, can support weight loss or maintenance efforts.Seaweed salad’s role in weight management is primarily attributed to its nutritional profile.
It is low in calories and fat, while being a good source of fiber and essential nutrients. The fiber content promotes a feeling of fullness, suppressing appetite and reducing the likelihood of overeating. The high water content further contributes to this satiety effect. Incorporating seaweed salad into a diet does not guarantee weight loss on its own; it must be part of a comprehensive approach that includes regular exercise and a balanced intake of other nutritious foods.
Seaweed Salad in Weight Management Meal Plans
Seaweed salad’s versatility allows for easy integration into various meal plans. For instance, it can serve as a low-calorie, nutrient-rich addition to lunch or dinner salads, replacing higher-calorie ingredients like creamy dressings or croutons. It can also be a refreshing side dish accompanying lean protein sources and vegetables. For individuals following a weight-loss plan, replacing a higher-calorie snack with seaweed salad can contribute to a daily calorie deficit.
For weight maintenance, seaweed salad provides a nutritious and satisfying option that helps manage hunger and prevents overconsumption of less healthy choices.
Calorie and Macronutrient Comparison of Seaweed Salad and Other Salad Ingredients
The following table compares the approximate calorie and macronutrient content per 100g serving of seaweed salad with other common salad ingredients. Note that values can vary depending on preparation methods and specific ingredients used.
| Ingredient | Calories (kcal) | Protein (g) | Carbohydrates (g) | Fat (g) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Seaweed Salad | 10-20 | 1-3 | 1-3 | 0.1-0.5 |
| Lettuce (Iceberg) | 15 | 1 | 2 | 0.2 |
| Cucumber | 15 | 1 | 4 | 0.2 |
| Cherry Tomatoes | 18 | 1 | 4 | 0.2 |
FAQ Compilation: Seaweed Salad Nutrition Facts
Is seaweed salad suitable for vegans and vegetarians?
Yes, seaweed salad is naturally vegan and vegetarian-friendly, providing a delicious and nutritious plant-based option.
Can I eat seaweed salad every day?
While generally safe, daily consumption might lead to excessive iodine intake. Moderation is key. Consult your doctor if you have concerns.
Where can I buy high-quality seaweed salad?
Look for reputable brands that prioritize sustainable sourcing and clearly label their products, specifying the seaweed type and origin. Asian grocery stores are often excellent sources.
Does seaweed salad taste fishy?
The taste varies depending on the seaweed type and preparation. Some varieties have a mild, subtly salty flavor, while others might have a more pronounced oceanic taste. Dressings and seasonings significantly impact the final flavor profile.
